- Map View
- Grid View
Activating Indigenous Peoples Water Rights Under the Cape York Water Plan (Cape York) 2019
This Situation Analysis Report details the current situation facing Cape York Aboriginal people seeking to understand and activate their water rights provided through Queensland’s statutory water planning process. The Water Plan (Cape York) 2019 and its Cape York Peninsula Heritage Act (CYPHA) reserve make 485,300ML of water available across 15 Cape York river catchments for Aboriginal corporations that perform Registered Native Title Body Corporate and/or Trustee of Aboriginal Freehold land functions. Under the Water Plan, where native title and Aboriginal freehold land rights and interests coincide in the same area of land, corporations that are the Trustee of Aboriginal Freehold land have priority for a water licence over Registered Native Title Bodies Corporate for the coincident area. A water licence nominating a volume of water and its conditions of use will be granted to eligible Aboriginal corporations upon application, where the water licence volume is calculated according to the volume of water available in the catchment and the percentage of the catchment area where the corporation holds an interest in land. An eligible Aboriginal corporation applying for and being granted a water licence is the first step in the process to activate the CYPHA water reserve. However, before water may be taken and used, the licence holder must apply to the Department of Regional Development, Manufacturing and Water (DRDMW) Chief Executive to amend their water licence. If approved by the Chief Executive, the licence will be amended to include a schedule of conditions regarding the taking and using of water. These conditions ensure issues such as environmental impacts and native title are considered prior to water being extracted from a watercourse and used for a land-based project. The licence holder may also apply to assign water to a third party, and if approved, this would enable water to be leased for a set period of time but not permanently traded. A desk top analysis to consider opportunities to activate CYPHA water for agriculture, aquaculture, energy production, mining, ecosystem services or municipal supply was undertaken, but few opportunities were identified. Cape York has relatively small areas of fertile soils, limited infrastructure and skilled labour and is remote from markets. Of the water use opportunities reviewed, mining and ecosystem services appear to be most prospective, although an ecosystems services market will need to be created before this opportunity could be meaningfully realised.

Education program
The CRCNA is supporting a vibrant education and training program through activities, educational experiences and professional development opportunities. It’s about enhancing the development and retention of research skills and capacity in areas aligned with CRCNA research themes for PhD, Scholars, Masters, Undergraduate and vocational students. Under the CRCNA’s Research Program 6: Industry-focused education and training program, the following research activities are underway with the objective of increasing technology development, skilled employees and research and development capacity within Northern Australia. 6.1 Postgraduate student programs 6.1.1 Postgraduate student scholarships for students enrolled in higher degree research programs in areas aligned with CRCNA research priorities. 6.1.2 Provide professional development opportunities for students, including industry mentoring, workshops, access to funding for travel and conference attendance, and access to funding for short courses/skills development. 6.2 Undergraduate student program 6.2.1 Undergraduate Scholarships for students enrolled in undergraduate programs in areas aligned with CRCNA research priorities. 6.3 Workforce development and training 6.3.1 Develop and implement programs which support, inform and build the capacity of the Northern Australian workforce and improve the wellbeing of northern communities. 6.3.2 Develop and implement a training program which supports, informs, and builds the capacity of the Northern Australian healthcare workforce in telehealth service delivery (Project Echo). 6.3.3 Develop and implement extension for community health outcomes program for mental health and telehealth practitioners and professionals (Project Echo). 6.3.4 Provide bursaries and sponsorships to support attendance at, or provision of, professional development opportunities which support, inform and build the capacity of the Northern Australian workforce and improve the wellbeing of northern communities in areas aligned with CRCNA research priorities.

Activating First Nation Water Rights under the Cape York Water Plan
The Cape York Water Plan 2019 sets aside 485,300 ML of water for Traditional Owners in Cape York under the Cape York Peninsula Heritage Act Reserve (Table 1).There is a lack of understanding, however, amongst Traditional Owners and their Corporations about their water rights and related opportunities with only two Aboriginal Corporations having applied for and been granted allocations. This project will build an understanding amongst Traditional Owners and their Corporations of their water rights and support them to access and utilise these rights. This project will also address the challenges other stakeholders have seeking to access and utilise these CYPHA allocations by providing information on the Aboriginal Corporations who hold these allocations and the process for engagement and leasing of water rights. The project will also inform broader reforms across Northern Australia in relation to strategic Indigenous reserves and inform other water policies and processes such as the refresh of the National Water Initiative.
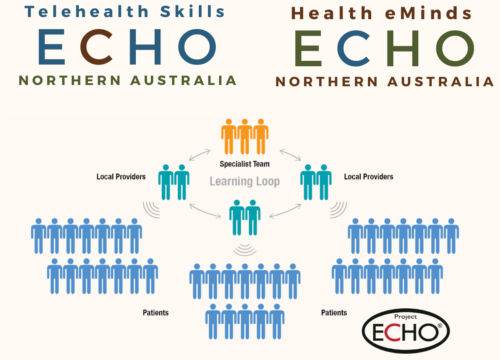
Project ECHO: Health eMinds and Telehealth Skills
Project ECHO The CRCNA, in partnership with the University of Queensland Centre for Online Health has developed two unique ECHO projects targeting Northern Australian healthcare workers. These are: Health eMinds ECHO Telehealth Skills ECHO Based on the Project ECHO model, we will deliver free monthly online sessions open to all healthcare professionals and staff working in Northern Australia. Project ECHO ® (Extension for Community Health Outcomes) is a virtual knowledge-sharing network designed to create a ‘learning loop’ between healthcare professionals and healthcare workers with the aim of increasing knowledge and access to quality healthcare in local communities. Project ECHO is an interactive model of collaborative learning through case discussions. In ECHO, professionals from across Northern Australia, including those in rural or under-served areas gain access to a panel of specialists through regular videoconferencing sessions. At every session, participants present de-identified cases for group discussion and gain advice from specialty experts, as well as other peers in the network. The group of multi-disciplinary healthcare workers form a community of practice, which serves as a sustainable mechanism for ongoing knowledge sharing and mentorship. Visit crcna.com.au/project-echo for all the information! Health eMinds ECHO The Health eMinds ECHO is a series of free, interactive case-based virtual mentoring sessions which address a range of topics related to the delivery of mental healthcare- in a range of healthcare settings across Northern Australia. Health eMinds ECHO sessions are open to anyone working in the delivery of mental health services in Northern Australia, including clinicians, front line and community support workers and allied healthcare workers. The CRCNA understands building a collaborative and interactive network of mental health care professionals and healthcare workers is an important part of improving service delivery and access to new models of care, especially for those in rural and remote and First Nations contexts. The Healthy eMinds ECHO is also about supporting mental healthcare workers, connecting peers and creating a community of best practice to inform high-quality care in the north. Access more information, including registration and resources for the Health eMinds ECHO Telehealth Skills ECHO The Telehealth Skills ECHO is a series of free, interactive case-based virtual mentoring sessions which address a range of topics related to the delivery of telehealth – in a range of healthcare settings. Telehealth Skills ECHO sessions are open to anyone working in healthcare in Northern Australia who are using or are considering implementing telehealth services. Access more information, including registration and resources for the Telehealth Skills ECHO

Aboriginal commercial fishing and aquaculture (WA)
This project builds upon existing Government support structures, research and identified industry needs to develop Aboriginal ownership and participation in WA Commercial fishing and aquaculture industries. The focus of this project is threefold: De-risking new commercialisation pathways for three identified key species (sea cucumber, mud crab and black lipped rock oyster) suitable from the Northern Gascoyne waters through to the Kimberley. An introductory workshop package on commercial fishing and aquaculture opportunities (regionally appropriate) delivered to salt water Aboriginal Corporations with authorized consent to operate on native title land/water Drawing implications from the project back towards a Northern WA-wide policy and planning approach towards de-risking for Aboriginal fishing and aquaculture, consistent with the WA aquaculture development plan.

Grain storage extension – Far North
As the developing far northern cropping regions of Australia expand their grain production, so too will grain storage requirements. Arguably, the most critical component of efficient grain storage is starting with the right facility, enabling grain quality to be maintained through good management. With growers investing in fit-for-purpose infrastructure, extension can then assist growers and industry on best practice management techniques to maintain grain quality during storage, preventing losses from mould, quality degradation and insect damage. As such, this project will take a multi-facet, whole of industry and supply chain approach to enable best management practices for maintaining the quality of grain under storage in the far north. An initial scoping study to identify specific requirements and challenges for grain storage in the far north will build on the knowledge and previous experience the team already has in the region. The team would then tailor extension material and develop resources specific to the region, focusing on the challenges and opportunities for storing grain in the far north. The aim of this project is to provide all grain growers, advisers and industry organisations access to the knowledge, skills and tools to: Make informed decisions to invest confidently in grain storage infrastructure Manage grain quality and storage pests proficiently and cost effectively Maintain and value add grain through processing, blending and segregation Enable access to higher value or closer markets to reduce freight costs Successfully integrate grain storage into livestock production enterprises for supplementary and drought feeding.

Ensuring best practice in the free range Buffalo supply chain
The project aim is to develop evidenced-based and feasible recommendations and strategies that improve the health and welfare outcomes for harvested buffalo throughout the entire supply chain. The project has four main objectives to achieve its purpose: 1. Analyse current evidence, practices, risk factors, and indicators of adverse animal mortality, health, and welfare outcomes throughout the free-range buffalo supply chain. 2. Evaluate the influence of animal-, management- and environmental-based factors on key animal welfare outcomes for a range of supply chain conditions. 3. Develop evidence-based and feasible recommendations for policy and practice changes that will reduce the risk of animal mortalities and adverse health and welfare outcomes. 4. Identify the opportunities for economically feasible buffalo harvesting on traditional lands whilst achieving acceptable animal welfare outcomes and meeting the economic development, cultural, and ecological goals of indigenous communities. The ultimate outcome of the project is to reduce mortality rates to comparable levels with the cattle industry across the supply chain and to meet the Australian Standards for Export of Livestock (ASEL 3.0, Department of Agriculture 2020) conditions. The project includes extensive engagement and consultation with industry, government, and indigenous stakeholders to understand the issues, review new evidence and explore feasible solutions and changes throughout the entire supply chain. The outcome of the supplementary work, which is covered by the fourth objective, will be a plan for sustainable harvest of buffalo across Arnhem Land that meets the aspirations of traditional owners and reduces the environmental impact of buffalo on sensitive areas.

Making Water Work program: Achieving reef water quality requirements in new agricultural developments
The project will assist the expansion of agriculture in the Lower Fitzroy (Central Queensland) by bridging the support gap to meet Reef Water Quality requirements. Businesses undergoing material change use will have access to advice and land management toolkits to navigate the regulatory constraints, monitoring and record keeping practices necessary for production and operation. This mechanism for continuous improvement will assist industry and tailored to specific regional needs.

Cotton Grains Cattle program: North Queensland farming systems
This project aims to co-design scalable diversification options and drought resilience practices for northern Queensland cotton, grain and cattle enterprises, and quantify the economic, social and environmental values and risks of these options. Whole farm level systems participatory research will examine: current farm resources and business performance co-designed time sensitive responses to drought and market volatility information and tools needed for adoption the impact of extreme climate events on productivity and sustainability the level of climate information accuracy and timeliness required for economic value how climate variability influences the risk of not adopting available solutions whole farm economic models for assessment of on-farm produced grains and/or forage crops when grown in cropping systems for cattle feed, existing environment stewardship frameworks alignment with north Queensland mixed farming systems, agri-business and community regional development vision and what are appropriate stewardship guidelines and self-assessment options for balancing the costs, legislation, social license and value chain demand and opportunities?

Black Jewfish: a new candidate for aquaculture in Northern Australia
Closing the life cycle of Black Jewfish Protonibea diacanthus: a new candidate for aquaculture in Northern Australia Black Jewfish aquaculture is in early stages of development and three batches of juveniles have been produced at the Darwin Aquaculture Centre in the Northern Territory. The initial primary bottlenecks identified are handling stress, larval survival, and management of cannibalism in early juvenile stages. The research questions this project will address are: What factors will be key in improving rearing procedures for black jewfish? Are black jewfish a suitable species for aquaculture? To address these questions, the project team will undertake a series of trials to determine optimum growing procedures for black jewfish in aquaculture systems. This requires access to high quality, fertilised black jewfish eggs, which is a limiting factor with current broodstock holding systems at the DAC. The addition of new broodstock (adult) housing capacity will increase availability of sexually mature fish and therefore fertilised eggs, enabling two annual spawns, around the black jewfish natural spawning season, to undertake larval rearing, nursery, grow-out and broodstock handling trials, targeted at developing and refining rearing protocols for black jewfish. The key areas of work for this project will include: Larval rearing trials which will focus on optimising nutrition, weaning and water quality procedures to increase survival. Nursery trials will be focused on reducing cannibalism and handling stress. Grow out trials will be performed on farms and will be focused on assessing and guidinghandling and feeding techniques. Broodstock trials will focus on animal handling for gonad assessment. Furthermore, as hatchery produced fish reach harvest size they will be assessed for end-product quality and marketability. This will all contribute to the primary final objective of the project, to assess the feasibility of black jewfish for commercial aquaculture and to produce the first hatchery manual for production.

Blacklip Rock Oyster industry development
This project will continue to build on the foundational work undertaken by researchers at the Darwin Aquaculture Centre, as part of an initial Tropical Rock Oyster research and development project (A.2.1819053NT). During the first phase of the CRCNA-funded project (2019-2023), significant progress has been made in this space, culminating in the development the world’s first hatchery manual for the Blacklip Rock Oyster (BRO). Over this period, hatchery production at the Darwin Aquaculture Centre (DAC) has increased exponentially (from 10,000s to 100,000s spat per spawning run). This increase in production is a direct result of improved hatchery techniques, which have been enhanced through broodstock conditioning, settlement and nursery trials conducted during the first project phase. However, as production has scaled up, new challenges have emerged in the nursery, resulting in inconsistent spat yields. Further research is required to continue to optimise production and reduce variability in spat production between spawning runs, which is critical to ensure farms can consistently access commercial quantities of advanced spat, and thereby build industry confidence and encourage private investment. The project will continue refinements to year-round supply of hatchery-reared spat (juvenile oyster) as this is fundamental to commercialisation, building confidence and encouraging investment. Extension and mentoring will be provided to support oyster farmers and Indigenous communities and farming trials across the Northern Territory.

Tropical Rock Oyster research and development WA
This project establishes a collaborative cross jurisdictional approach to address the most significant technical and regulatory issues that confront the fledgling Tropical Rock Oyster (TRO) industry. The project aims to examine and resolve several key issues to support the development of the TRO industry by undertaking sub-projects addressing the different research needs identified: Securing commercial spat supply – will utilise existing hatchery infrastructure and expertise at the DPIRD Hillarys facility to refine culture techniques for the Blacklip Rock Oyster (BLRO) and other TRO species to be identified in WA. Researchers will employ standard hatchery protocols used in the production of SROs on the TRO species identified in the Pilbara and Kimberley and compare performances before moving the experiment to ocean-based nurseries. Optimisation of grow-out methods and gear technology – Grow-out trials will take place in the Kimberley (Cone Bay) and in the Pilbara (three sites selected in the Dampier Archipelago) at sites providing intertidal and subtidal conditions for the farming of new TRO species (and BLRO in the Kimberley). These trials will include work to: identify TRO species with good aquaculture potential and what system (intertidal or subtidal) they should be cultured with. compare the performance of a maximum of three TRO species (likely to be two species) during grow out in order to select the best performing species. industry road testing the different grow out scenarios for new TRO species. The project team worked cross-jurisdictionally with researchers from the Darwin Aquaculture Centre working on project A.2.1819053NT. Outcomes This project has developed identification tools and agreed common names for key commercial tropical oyster species to prevent potential market confusion and ensure accurate licencing and management of the emerging industry. The Darwin Aquaculture Centre has developed a hatchery manual for the Blacklip Rock Oyster (Saccostrea echinata). In April 2023, more than 700,000 mature oysters grown as part of this research project were transferred to commercial partner Maxima. Maxima will continue refining grow-out techniques with the aim to scale up to commercial harvest within the next decade.

